Calorie Difference Bettween Cooked Ground Beef and Turkey

vs

SUMMARY
Beef and turkey are generally similar in poly peptide and cholesterol content. However, beefiness contains approximately two times more fats. They both are rich sources of different vitamins and minerals.
Neither turkey nor beef is healthier than the other, simply peel-free turkey is benign for decreasing cardiovascular, diabetes, and cancer risks.
Table of contents
- INTRODUCTION
- MEAT CUTS
- Nutrition
- Protein
- Fats
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- HEALTH IMPACT
- Cardiovascular health
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- References
INTRODUCTION
Turkey or beef? Information technology is often hard to determine what to eat and what is healthier. The kickoff one is the world's second almost popular poultry meat, but the second one is more traditional. Hither we volition explore the 2 from a scientific perspective focusing on nutrition and health.
Beef is classified as red meat due to its high content of myoglobin and therefore fe. Turkey is considered white meat and is lighter in color, so information technology has a lower content of myoglobin and iron leap to it. The main difference between these two kinds of meat is noticeable to the blind eye.
MEAT CUTS
Meat characteristics can vary depending on the conditions they kept the animal in, the age or weight, and other aspects.
The turkey tin exist divided into 3 main parts: the breast, the wings, and the legs. The chest and fly meat tend to be lighter, while the leg meat is darker. It is and so because the turkey is a flightless bird, and its leg muscles are improve developed.
Depending on its location, beef is also divided into some parts: the chuck (shoulder), the brisket and shank (breast), the rib, the sirloin (hip), the curt loin, the brusk plate, the flake, and the circular (2). All the types of meat mentioned take different qualities and differ by training methods.
Nutrition
Here we will compare the nutritional values of a roasted whole turkey with meat and skin and a broiled basis beef, consisting of 85% of lean meat and fifteen% of fatty. It'due south important to remember that the nutritional values of the meats specified here may differ from those of other varieties.
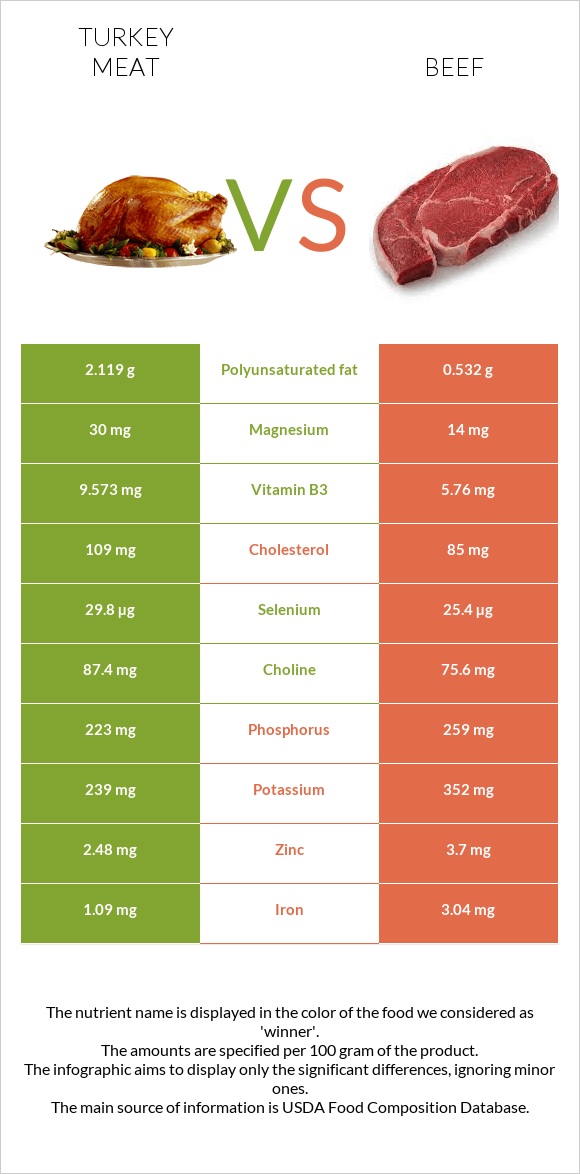
Turkey meat is richer in proteins, while beef contains more calories. Both of them do not contain a significant number of carbohydrates.
Beef contains less cholesterol than turkey. They both are rich in vitamins of group B.
Now we will have a closer look at every kind of nutrient present in these types of meat.
Protein
Animal protein usually contains all nine essential amino acids needed for the growth of the trunk. Both beef and turkey meat are skillful sources of protein.
Turkey contains 28.5g of protein in a 100g serving (3), while beef provides 25.9g of it (iv). Sirloin is the beef cut with the highest poly peptide content. For health-conscious steak eaters, it's 1 of the best options.
When beefiness is processed, its proteins suffer a nifty deal of damage.
Beef sausages and steaks, on average, offering 2 times less poly peptide than baked, ground beefiness. The protein composition of the turkey does not usually alter during processing.
Every bit a source of essential amino acids, turkey meat is rich in lysine, leucine, and tryptophan (v). Beefiness contains a notable amount of lysine, leucine, and valine (vi). The protein constitute in both of these meats has significantly high quality.
Fats
Compared to turkey meat, beef is almost two times higher in fats. The 100g serving of beef provides 15.4g of fats, while the same corporeality of turkey contains 7.39g of lipids. At that place is a direct proportion in the processing of meat and fat content. Processed turkey items, such as sausages and salary, have well-nigh 2-3 times the fat content of unprocessed turkey products. Beef likewise follows this trend.
Despite beingness higher in fats, beef is lower in cholesterol. The Cholesterol corporeality in 100g of beef is 90mg, while the aforementioned portion of turkey contains 109g of it. You should know that the fat of turkey is primarily located in its skin; therefore, removing the skin ways reducing the fatty intake. The fattiest section of the beef is the rib. For this reason, it has the highest content of calories and saturated fats. It should be baked under loftier temperatures for fats to be cooked.
Vitamins
Turkey meat is an excellent source of B complex vitamins. It is higher in vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6. Turkey is peculiarly rich in vitamin B3 (niacin) and provides virtually two times more of it per serving. nine.573mg of niacin is found in a 0g of turkey, while the aforementioned amount of beef contains 5.378mg of it.
On the other hand, beefiness covers approximately lx% of vitamin B12 daily needs. And then, when you enjoy burgers or steaks, your favorite cut of beefiness offers lots of vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Vitamin comparing score is based on the number of vitamins by which ane or the other food is richer. The "coverage" chart below show how much of the daily needs can be covered past 300 grams of the food
![]()
6
:
4
![]()
Contains more Vitamin A +333.3%
Contains more Vitamin D +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B2 +59.7%
Contains more Vitamin B3 +78%
Contains more than Vitamin B5 +44.1%
Contains more Vitamin B6 +61.3%
Contains more than Vitamin Due east +71.4%
Contains more Vitamin B12 +158.8%
Contains more than Vitamin K +∞%
Equal in Vitamin B1 - 0.046
Equal in Folate - nine
Contains more than Vitamin A +333.iii%
Contains more Vitamin D +∞%
Contains more Vitamin B2 +59.7%
Contains more than Vitamin B3 +78%
Contains more Vitamin B5 +44.1%
Contains more than Vitamin B6 +61.3%
Contains more than Vitamin E +71.4%
Contains more Vitamin B12 +158.8%
Contains more Vitamin K +∞%
Equal in Vitamin B1 - 0.046
Equal in Folate - 9
Minerals
Turkey and beef provide nearly all the essential minerals, each of them at different levels. Beef has a considerably high amount of Atomic number 26, Zinc, Calcium, and Potassium, but the turkey is richer in Magnesium, Phosphorus, and Sodium.
Before existence prepared, some turkey products, such as bacon, are cured with sodium nitrate. Therefore, turkey bacon has a higher salt content. Processed beef'south sodium content is also high. It can upshot in cardiovascular problems. Every bit a result, you should pay attention to the salt content of processed meat products.
Mineral Comparison
Mineral comparison score is based on the number of minerals past which one or the other food is richer. The "coverage" chart below show how much of the daily needs can exist covered by 300 grams of the food
![]()
3
:
v
![]()
Contains more Magnesium +42.9%
Contains more Phosphorus +12.6%
Contains more Calcium +28.6%
Contains more Iron +138.v%
Contains more Potassium +33.1%
Contains less Sodium -30.i%
Contains more Zinc +154.4%
Contains more than Magnesium +42.9%
Contains more Phosphorus +12.6%
Contains more Calcium +28.half dozen%
Contains more Iron +138.5%
Contains more Potassium +33.1%
Contains less Sodium -xxx.i%
Contains more Zinc +154.4%
HEALTH Impact
Cardiovascular health
It is debatable how ruby-red meat, such as beef, contributes to cardiovascular affliction. A likely contributor is the saturated fat content in cherry meat. The American Health Association recommends limiting the amount of ruddy meat in the everyday diet.
Furthermore, fats are not the merely cause of heart diseases present in carmine meat. Beefiness contains carnitine and choline, and when being processed in the human gut, these compounds produce a chemic called trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO). High levels of TMAO in the blood increase the take chances of heart assail, stroke, and hardened arteries (7).
In dissimilarity, poultry meat, such as turkey, decreases cardiovascular take chances (viii). It may be explained by the lower fats, heme iron, and sodium in white meat. Turkey meat is the winner of this category.
Diabetes
Almost studies testify that red meat and poultry increase the risk of developing diabetes. People who use meat have a higher probability of developing diabetes than those who do not consume meat at all.
People with diabetes should avoid loftier fat and candy meat products. They should not use prime cuts of beef, such as ribs. Lean turkey breast meat without the skin is improve (9).
The risk of diabetes mellitus type 2 is too continued to the training method of meat. When cooked at a high temperature, the risk increases - grilled, roasted, or barbequed (x). Hence, cooking methods at moderate temperatures, similar boiling, steaming, or stir-frying, are recommended.
Cancer
At that place is a negative link between cherry-red and processed meat consumption and cancer. The American Cancer Social club claims that colorectal cancer is the primary reason for limiting these products in everyday nutrition (xi).
Conversely, poultry meat tends to decrease the gamble of esophagus, liver, colorectal, lung, and breast cancer. Substitution of ruby meat with white meat is beneficial from a cancer-preventing perspective.
References
- https://national4hpoultry.ca.uky.edu/marketpoultry/partsID
- https://ediblekentucky.ediblecommunities.com/recipes/locavores-guide-beefiness
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171479/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174032/nutrients
- https://foodstruct.com/food/turkey-meat
- https://www.rjpbcs.com/pdf/2016_7(iv)/%5B161%5D.pdf
- https://world wide web.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6213249/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322959346
- https://uamshealth.com/nutrition/diabetic-diet-meat-choices/
- How Meat Is Cooked May Affect Gamble of Type 2 Diabetes
- http://pressroom.cancer.org/index.php?southward=20296&particular=29968
Infographic
Which nutrient is preferable for your diet?
![]()
![]()
is better in example of low diet
 |  | |
| Low Fats diet | | |
| Low Carbs nutrition | | |
| Low Calories diet | | |
| Low glycemic index diet | Equal | |
People also compare
Vitamin and Mineral Summary Scores
The summary score is calculated by summing upward the daily values independent in 300 grams of the product. Obviously the more the nutrient fulfills human daily needs, the more the summary score is.
Vitamin Summary Score
50
![]()
52
![]()
Mineral Summary Score
37
![]()
55
![]()
Macronutrients Comparison
Macronutrient comparison charts compare the amount of poly peptide, total fats, and total carbohydrates in 300 grams of the food. The displayed values show how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of nutrient.
Protein
171%
![]()
156%
![]()
Carbohydrates
0%
![]()
0%
![]()
Fats
34%
![]()
71%
![]()
Comparison summary
Which food is lower in Saturated Fat?
![]()
Turkey meat is lower in Saturated Fatty (difference - 3.74g)
Which food contains less Sodium?
![]()
Beef contains less Sodium (difference - 31mg)
Which nutrient is lower in Cholesterol?
![]()
Beef is lower in Cholesterol (departure - 21mg)
Which food contains less Saccharide?
?
The foods are relatively equal in Sugar (0 g)
Which food is lower in glycemic index?
?
The foods have equal glycemic indexes (0)
Which food is cheaper?
?
The foods are relatively equal in price ($two)
Which nutrient is richer in minerals?
?
It cannot be stated which nutrient is richer in vitamins. See the charts below for detailed information. See the charts beneath for detailed information. Come across the charts below for detailed information.
Which food is richer in vitamins?
?
It cannot be stated which nutrient is richer in vitamins. See the charts below for detailed information. See the charts beneath for detailed data. Run across the charts below for detailed information.
fleetwooddomay1984.blogspot.com
Source: https://foodstruct.com/compare/turkey-meat-vs-beef

0 Response to "Calorie Difference Bettween Cooked Ground Beef and Turkey"
Enregistrer un commentaire